|
|
 Measure the circumference of each living tree in your yard at a height of 4.5 feet
(4 feet, 6 inches) above the ground level. Measure the circumference of each living tree in your yard at a height of 4.5 feet
(4 feet, 6 inches) above the ground level.
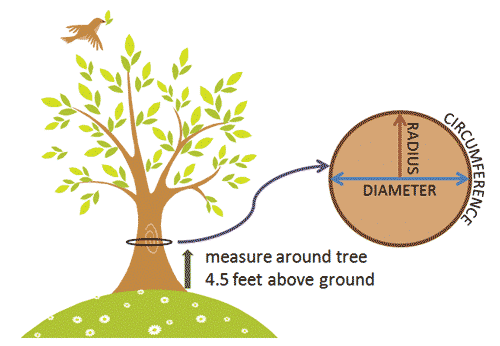
Calculating the circumference of a tree
CIRCUMFERENCE
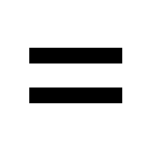 2
2
  RADIUS
RADIUS
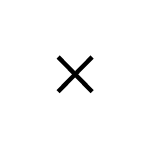
if you know the CIRCUMFERENCE, you can calculate the RADIUS
RADIUS
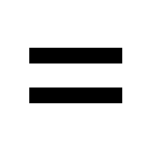 CIRCUMFERENCE
CIRCUMFERENCE
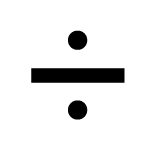 (2
(2

 ) )
If you know the RADIUS, you can calculate the
DIAMETER
DIAMETER
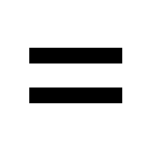 2
2
 RADIUS
RADIUS
 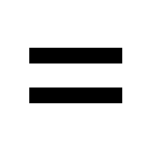
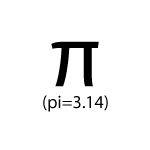
3.14
|
 Enter the number of trees within each size class. Enter the number of trees within each size class.
|